SAML Authentication & Security | FGRADE
Secure identity exchange with FGRADE SAML -fast, reliable, and compliant authentication for modern enterprises.
About security assertion markup language (SAML)
Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML) is an XML-based standard that enables Single Sign-On (SSO) between an identity provider (IdP) and service providers (SPs).
Instead of multiple logins, users sign in once, and SAML securely shares authentication data across apps using digitally signed assertions.
This improves security through centralized authentication, supports MFA, and gives users a faster, seamless sign-in experience. The current standard is SAML 2.0.MDM solutions operate from a centralized console, giving IT administrators the ability to manage the entire device lifecycle, from initial onboarding to eventual retirement. This includes managing both company-owned devices and personal devices used for work. By providing capabilities like mandatory security settings, remote provisioning of applications, and instant data security controls, MDM ensures that a highly mobile workforce remains productive without compromising sensitive corporate data. It is the essential framework for maintaining security, compliance, and operational efficiency in the age of mobility.
How does Security Assertion Markup Language work?
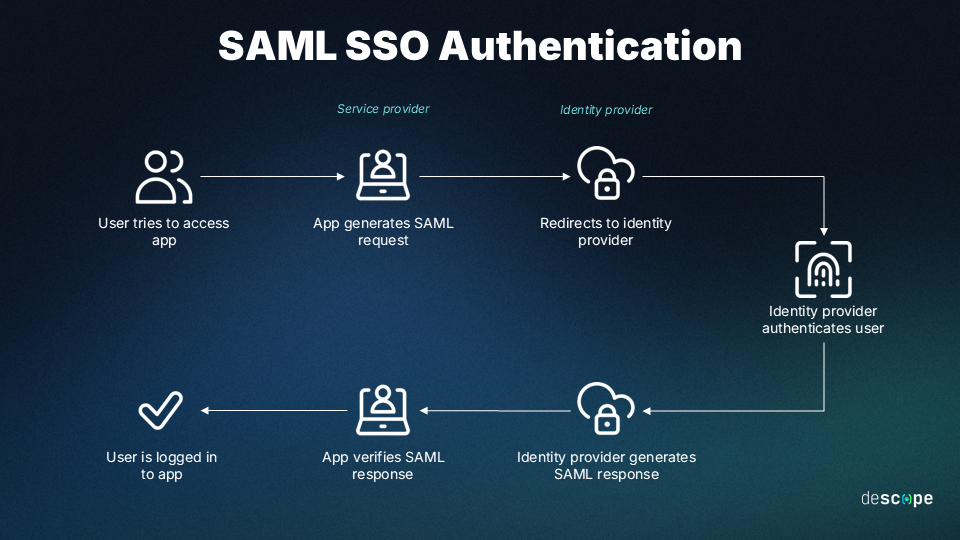
Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML) authentication builds a trust relationship between the Service Provider (SP) and the Identity Provider (IdP) to enable Single Sign-On (SSO).
1. Access request: User tries to open a protected app (SP).
2. Redirection: SP redirects the user to IdP with a SAML Request.
3. Login: IdP authenticates the user or uses an active session.
4. SAML Response: IdP creates and signs a SAML Assertion with user details.
5. Delivery: Browser sends the assertion to the SP’s ACS URL.
6. Validation: SP verifies the signature, extracts user info, and grants access.
This secure flow lets the IdP handle authentication, improving security, centralizing login, and simplifying user access across apps.

Types of SAML providers
SAML authentication involves the interaction of three main roles, two of which are providers:
• Principal (User): This is typically the human user (or subject) attempting to access a resource.
• Identity Provider (IdP): The system responsible for authenticating the user. It manages user identities, handles the login process, and issues the SAML assertion. Examples include Microsoft Entra ID (formerly Azure AD), Okta, and Google Workspace.
• Service Provider (SP): The application or web service (the resource) the user is trying to access. It relies on the IdP's assertion to authorize the user and grant access, thereby offloading the credential management burden. Examples include cloud-based business applications like Salesforce or Slack.
What is a SAML Assertion?
A SAML Assertion is an XML document that contains a verifiable statement from the Identity Provider to the Service Provider about a user. It’s the core data structure that carries the necessary information to enable Single Sign-On. The assertion is digitally signed by the IdP to guarantee its source, integrity, and authenticity.
SAML defines three main types of statements that can be contained with an assertion.
1. Authentication Statement: Asserts that the principal was authenticated by the IdP at a specific time and using a particular method.
2. Attribute Statement: Provides specific information, or attributes, about the user, such as their email address, name, roles, or department. This data is often used by the SP for authorization or personalization
3. Authorization Decision Statement: Declares whether a request by the user to access a specific resource has been granted or denied by the IdP.
The SAML assertion also contains other critical elements like an Issuer, a Subject, and Conditions that the SP must verify for the assertion to be considered valid.
Discover how SAML can streamline your business
Reach out to the FGRADE Concierge Team for a free consultation!
Call Us
+91 916 056 5554
Mail Us
sales@fgrade.com
Why Choose FGrade?
01
Migrations
FGrade handles seamless migrations to ensuring your data is transferred accurately and securely. Our successful track record speaks for itself.
02
Certified Experts
Our team comprises certified professionals with extensive training in all IT products. Trust us to manage your HR systems with the utmost expertise.
03
Great Price Discounts
At FGrade, we're ready to help you implement SAMLconfidently, customizing workflows, setting up approvals all these at lower prices.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML)?
SAML (Security Assertion Markup Language) is an open standard, XML-based protocol for exchanging authentication and authorization data between an Identity Provider (IdP) and a Service Provider (SP). It is the technical foundation that enables users to achieve Single Sign-On (SSO), allowing them to log in once to access multiple applications securely.
What are assertions in SAML?
SAML Assertions are the core XML documents created by the Identity Provider (IdP) and sent to the Service Provider (SP). They are digitally signed statements that assert facts about a user's identity, such as:
1. Authentication (proof the user logged in).
2. Attributes (user details like email, roles).
3. Authorization Decision (whether access to a specific resource is granted or denied).
Is Writer compatible with Microsoft Word?
The three primary roles in a SAML transaction are:
1. The Principal (or Subject): Typically the user (e.g., an employee) attempting to access a service.
2. The Identity Provider (IdP): The system that authenticates the user and issues the SAML assertion (e.g., Okta, Microsoft Entra ID).
3. The Service Provider (SP): The application or service the user wants to access, which relies on the IdP's assertion to grant access (e.g., a cloud-based CRM tool).
What is the main purpose of SAML?
The main purpose of SAML is to enable Single Sign-On (SSO) and federated identity management for web-based applications. It standardizes the secure exchange of user authentication and authorization information between different, independent security domains (the IdP and SP), simplifying the user login experience and centralizing security control for enterprises.
What is SAML vs SSO?
SSO (Single Sign-On) is the outcome or capability—it's the feature that allows a user to log in once and access multiple applications without re-entering credentials. SAML is the protocol or technical standard that makes one type of web-based SSO possible. In short, SAML is one of the key languages or frameworks used to implement the SSO feature.

Search, compare & buy top business software with FGRADE. Find the best deals on Microsoft 365, Zoho, Google Workspace & more. Shop smart & save big!
Office Address
AWFIS, Ground Floor, DSL abacus it park, Survey Colony, Industrial Development Area, Uppal, Hyderabad, Telangana 500039








